Which Type Of Template Creates A Traditional Access Database
Introduction
Databases are an organized drove of related data records. Database management systems manage and dispense data inside a database.
There are many different approaches to storing and modeling data, resulting in various types of databases.
This commodity provides an in-depth overview of the different database types bachelor.
Database Types
In that location are many different approaches to analyzing the different database types available. The tabular array below provides a full general overview of the various types currently available:
| Based On | Database Types |
|---|---|
| Model | Relational Non-Relational (NoSQL) Object-oriented |
| Location | Centralized Distributed |
| Pattern | Operational (OLTP) Analytical (OLAP) |
| Hosting | On-Premises Deject |
| Processing Power | Personal Commercial |
The diverse database types combine to create a specific environs. For example, a non-relational distributed commercial database describes the model, location and processing of the database respectively.
Note: For more data on the design and the difference between Operational (OLTP) and Analytical (OLAP), delight visit our article OLTP vs. OLAP.
Database Model Types
The three general database types based on the model are:
1. Relational database
two. Non-relational database (NoSQL)
3. Object-oriented database
The deviation betwixt the models is the way the information looks inside the database. Consequently, each model type has a different management system and data relationships.
Relational Database
The relational database model is the most extensively used besides as the oldest database blazon. The three critical components of a relational database are:
- Tables. An entity type with relations.
- Rows. Records or instances of an entity type.
- Columns. Value attributes of instances.
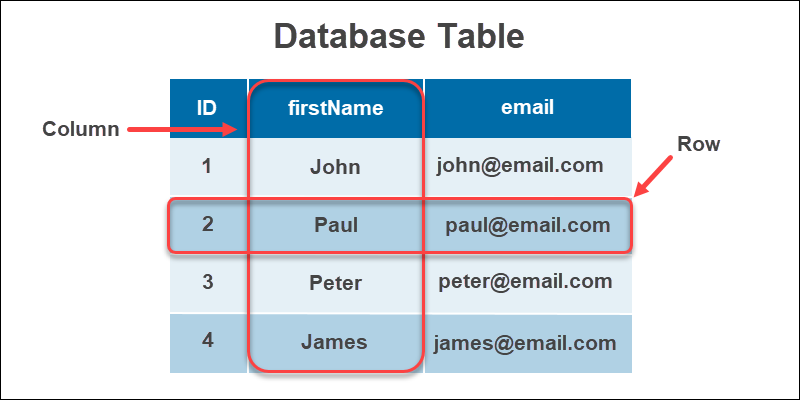
A relational database provides a fix of data rows in response to a query. A query language, about unremarkably the Structured Query Language or SQL, helps create these data views.
Relational Database Features
The principal features of a relational database are:
- Acid compliant. The database retrains integrity while performing transactions.
- Range of data types. Provides the adequacy to store any data equally well as carry out complex queries.
- Collaborative. Multiple users are able to access the database and work on the same project.
- Secure. Admission is limited or restricted through user permissions.
- Stable. Relational databases are well-understood and documented.
What are Relational Databases Used For?
Relational databases are the most implemented database type. In that location are many use cases, some of which include:
- Online transaction systems. The database supports many users besides as frequent queries needed in online transactions.
- IoT. Relational databases are lightweight and have the processing power needed for edge calculating.
- Data warehouses. The critical component of the data warehouse architecture is storage. Relational databases are easily integrated and optimized for massive queries from multiple sources.
Almost Popular Relational Databases
There are countless commercial as well as open-source databases. The meridian 10 most popular relational databases are:
1. Oracle
ii. MySQL
three. Microsoft SQL Server
iv. PostgreSQL
5. IBM Db2
6. SQLite
7. Microsoft Access
8. MariaDB
9. Hive
10. Microsoft Azure SQL Database
Not-relational Database (NoSQL Database)
A non-relational database, or NoSQL ("Not Merely SQL"), is a blazon of database that models and stores data differently from relational databases. Instead of tables, non-relational databases model relationships between data in an alternative way.
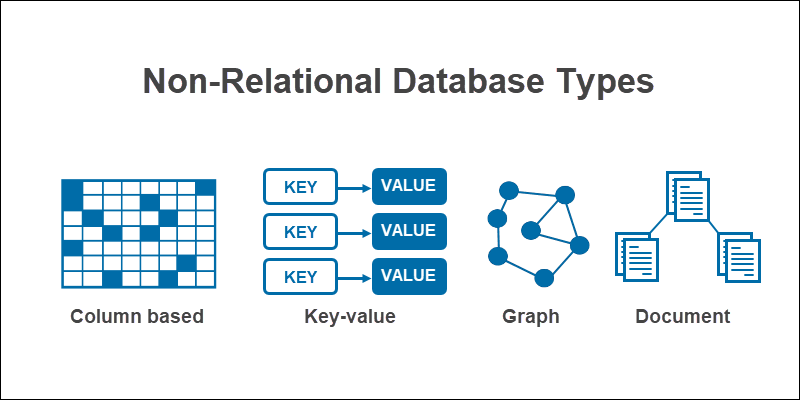
The 4 NoSQL database types are:
- Certificate
- Fundamental-value
- Column based
- Graph
Not-relational Database Features
The main features of non-relational databases are:
- Flexible. Handling structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data is a breeze with non-relational database types.
- Scalable and responsive. Massive information storage scales well with on-demand servers and provides quick query responses.
- Zero downtime. High availability for minimal downtime due to most real-time information replication.
- Cloud compatible. The scalability of a cloud calculating architecture incorporates perfectly with non-relational databases.
- Multiple data structures. Different information types, as well equally multi-model database formats, are available.
What are Not-relational Databases Used For?
Non-relational databases perform best with variable information structures and massive amounts of data. Some use cases include:
- Real-time systems. A non-relational database combines the operational and belittling database systems into one. Whether feeding operational data into Hadoop or serving analytics results from Hadoop, not-relational databases provide the agile real-time experience.
- Personalized experience. Elastic scaling accommodates the massive amounts of data needed for any customized feel.
- Fraud detection. Loftier operation is vital in fraud detection. Non-relational databases are responsive and reliably meet the depression latency requirements of financial systems.
Most Popular Non-Relational Databases
The ten most popular non-relational databases are:
one. MongoDB
two. Redis
iii. Cassandra
4. HBase
5. Neo4j
6. Oracle NoSQL
7. RavenDB
8. Riak
9. OrientDB
ten. CouchDB
Object Database
An object database similarly represents information to objects in object-oriented programming. The critical components of an object-oriented database are:
- Objects. The basic building blocks for storing information.
- Classes. The schema or blueprint for an object.
- Methods. Structured behaviors of a form.
- Pointers. Access elements of a database and establish relations between objects.
Object databases combine object-oriented programming concepts with database capabilities.
Object Database Features
The main features of object databases are:
- Acrid transactions. All transactions are consummate without conflicting changes due to Acrid compliance.
- Transparent persistency. Object databases integrate seamlessly with object-oriented programming languages.
- Complex and custom data types. User-defined classes allow for custom too as complex information types to exist.
- Attainable. Information is easy to save and think.
- Easier modeling. Real-world problems and information are more than closely related to objects, which makes complex bug easier to model.
What Are Object Databases Used For?
Object databases perform best with circuitous data types, where one entity includes a massive amount of information. Some everyday use cases for this database model type are:
- Loftier-performance applications. Applications where fast data retrieval is vital to benefit from object databases since information is stored and retrieved as-is.
- Scientific purposes. Scientific data, also as calculations, are complex. Storing complex information and quick retrieval observe use in all kinds of scientific disciplines.
- Circuitous data structures. Due to permanent persistence with objects, database storage and expansion of circuitous data is accessible, eliminating the need to rework the database model.
Nearly Popular Object Databases
Currently, the top x most popular object databases are:
one. DB4o
2. ObjectStore
3. Matisse
four. Gemstone/Southward
five. ObjectDB
6. ObjectDatabase++
vii. Objectivity/DB
viii. Versant
9. Perst
10. Jade
Database Types Based on Location
Database types also differ based on the physical location of the storage.
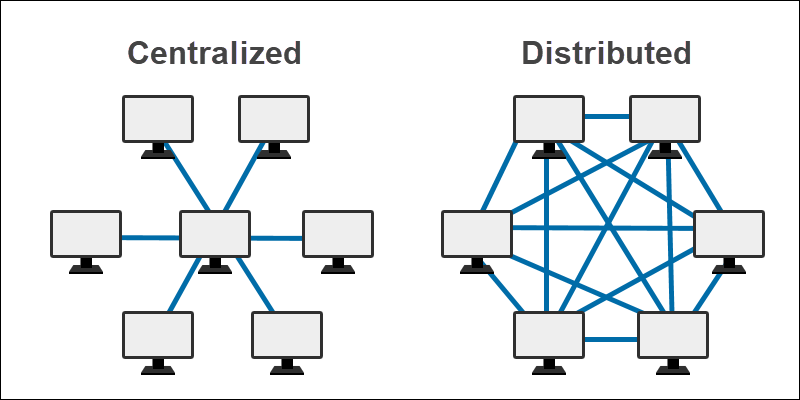
The two groups based on location are:
ane. Centralized databases
two. Distributed databases
Centralized Database
A centralized database is stored as well every bit managed in a single location. The information is bachelor through a network. The end-user has access through the network to the centralized computer, where the stored information resides.
Centralized Database Features
The main features of a centralized database are:
- Data integrity. Keeping data in i location maximizes data integrity and reduces redundancy. Data accuracy and reliability are enhanced.
- Security. A single betoken of location provides only one access point, leading to increased data safety.
- End-user friendly. Information admission, as well as updates, are immediate with a centralized database. A unmarried database design provides simplicity.
- Cost-effective. The labor, power supply, and maintenance are all reduced to a minimum through a centralized system. The database is easier to maintain from an assistants aspect.
- Information preservation. A error-tolerant setup through disaster recovery solutions.
What Are Centralized Databases Used For?
The benefits of a centralized database are nigh noticeable with large institutions. Some utilize cases include:
- Enterprise management. Big organizations use centralized databases to get a better overview of all the data.
- Government data. Centralized databases are prevalent in government organizations. One access point ensures data security.
- Schools and universities. Educational institutions make utilize of centralized databases. The maintenance is cost-effective, and the data stays accurate.
Distributed Database
Distributed databases shop information across unlike physical sites. The database resides on multiple CPUs on a single site or spread out across diverse locations. Due to the connections between the distributed databases, the information appears equally a single database to terminate-users.
Distributed Database Features
The nearly exciting features of a distributed database are:
- Location independency. The physical location of the database spreads out beyond multiple sites.
- Query processing distribution. A circuitous query splits into multiple sites, which divides the tasks betwixt different CPUs, reducing bottleneck.
- Distributed transactions. Multiple storage locations provide a distributed recovery method. Commit protocols be in cases of numerous transactions.
- Network linking. The distributed databases interlink through a network where communication happens between the storages as well equally with end-users.
- Seamless integration. Although not physically connected, distributed database parts connect into i logical database.
What Are Distributed Databases Used For?
Distributed databases work best in environments with many sectors where companies should limit the available information to reduce redundancy. Some examples include:
- Large companies. Most company sectors exercise not need a complete overview of data. Distributed databases help reduce the redundancy of information with individual departments.
- Global enterprises. Due to location independence, this database type fits well with companies with multiple sites.
Database Types Based on Design
The pattern of the storage depends on the business objective. There are two main approaches to database blueprint based on the function are:
ane. Operational (transactional) database
2. Analytical database
Although the databases serve a dissimilar purpose, incorporating the 2 together creates a data warehouse system.
Operational Database
An operational database manages and controls the key operations inside a concern. The database is known as an online transaction processing or OLTP database. The information collected directly from the source in real-time, providing a view of daily transactions.
Operational Database Features
Operational databases have the following features:
- Acrid compliant. Preserving the accuracy and integrity of each transaction is necessary for data organization.
- Fast processing. Operational databases require fast processing due to thousands of simultaneous requests.
- Small storage. Transactional data is merely stored temporarily. Therefore, operational databases serve equally a steppingstone before the data is archived.
- Regular backups. Collecting and storing information requires abiding backups, making legal compliance an essential cistron.
Belittling Database
Analytical databases provide a unified view of all information available within a business organisation. A complete overview of information inside a database is essential for planning, reporting, and making decisions. The database is known every bit an online analytical processing (OLAP) database.
Analytical Database Features
The features of an analytical database are:
- Distributed workload. The data comes from different operational systems distributed across nodes.
- Multi-dimensional. Enterprise information gains dimensionality through data aggregation and complex queries across databases.
- Query performance. Data denormalization improves query functioning for fourth dimension-intensive actions.
- Horizontal scalability. Analytical databases must scale out every bit the requirements for an enterprise to abound.
Database Types Based on Hosting
At that place are multiple hosting options for databases. The ii places where an information system resides are:
ane. On-bounds databases
two. Cloud databases
The notable difference between the two options is the availability of resources when the database deployment happens. For more than information on how the two approaches compare, check out our commodity: On-Premise vs. Cloud: Which is Right for Your Business?
On-premises Database
An on-bounds database resides in-firm. All the software, infrastructure likewise equally administration needed for support is local. With large-scale enterprises, the storage grows to a local data eye.
On-premises Database Features
The notable features of on-premises databases are:
- Security. Due to the infrastructure being in-house, on-premises databases are the best solution for storing sensitive information.
- Control. The enterprise is in complete control over the available information, providing a high level of regulation and privacy over the data.
- Compliance. Regulatory controls, such as HIPAA compliance, require knowing the location of sensitive data at whatsoever given moment.
Cloud Database
A cloud database is a hosting solution given past a third-party provider. The pay-as-go solution provides the database-as-a-service, avoiding the need to fix up a data eye physically. The active approach minimizes the initial investments needed to acquire data space while quickly expanding as more resources are required.
Cloud Database Features
The best features of a deject database are:
- Scalability. Cloud databases are flexible. Increasing or decreasing resources is quick due to virtualization.
- Management flexibility. The provider manages this database type, which in turn minimizes the management needed from the client. However, at that place are also options for outsourcing maintenance.
- Cost. With a deject database, yous only pay for what y'all need. The cost of investing in technical staff, as well equally maintenance, is minimized.
Database Types Based on Processing Power
The database processing depends on the business model. Choosing the wrong level of a database system affects the workflow of an system and team. Almost database vendors offer multiple solutions to database processing. The 2 main ones are:
1. Personal database
2. Commercial database
Businesses leverage the ability of both depending on the use case.
Personal Database
Personal databases accept single-user access and process on depression to medium-powered machines. Simpler database applications benefit from this database type due to the depression price and maintenance.
Commercial Database
A commercial database has multiple users with various permissions likewise as numerous applications on high-powered machines. High availability commercial databases are costly and require constant maintenance as well as support.
Conclusion
You should take a clear idea of the dissimilar database types bachelor and which one to use.
All database types accept their corresponding usage domain. None of the database types are a replacement for a unlike kind of database, and using multiple systems provides versatility over information management.
To learn how to create, retrieve, update and manage data in a database, brand sure to read our article DBMS - top 25 database direction systems.
Was this article helpful?
Yep No
Which Type Of Template Creates A Traditional Access Database,
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/database-types
Posted by: stoneboad1945.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Type Of Template Creates A Traditional Access Database"
Post a Comment